After Two Decades Undercover, She’s Ready to Tell the Real Story of Human Trafficking
O
n an August night in 2003, a young woman who went by the name Paulina sank into the sofa of her modest, rented apartment, opened up her laptop, and began talking about sex with a man she’d recently met in a Yahoo chat group. His name was Stephen Bolen. His first communications had been terse, but he soon warmed to Paulina. It didn’t take long for both of them to begin to open up.
Paulina had told Bolen she lived in the Atlanta area, that she had a three-year-old daughter, that her daughter’s father was no longer in the picture. Soon, she was sharing more intimate details: what it was like growing up a skinny white girl in a rough neighborhood outside of D.C.; how her dad, a Marine, had died by suicide two weeks before she was born; how her mom had been emotionally and physically abusive, and had never really shown her love. How she’d had a sexual relationship with her stepfather.
Paulina would put her daughter to bed and then she and Bolen would chat throughout the night, over Yahoo and sometimes on the phone. The back-and-forth could feel like dating, but with an added element of danger and risk: Both Paulina and Bolen knew they were tiptoeing up to a line to see if they trusted each other enough to cross it. It could take a while to figure that out.
Eventually, Bolen asked Paulina to send pictures of her daughter, and she agreed to do so, though the ones she’d shared were chaste — the little girl clothed and her face turned away from the camera or obscured behind an untamable halo of blond curls. After seeing the pictures, Bolen asked to meet. While a lot of the men Paulina had encountered in chatrooms like “Sex With Younger” just wanted to trade images and videos of children, to expand their illicit collections, Bolen was a “traveler,” someone looking to act upon his obsessions.
On Sept. 17, just as they’d arranged, Paulina sat on a bench outside Perimeter Mall with a stroller parked in front of her, scanning the parking lot nervously. Part of her hoped Bolen wouldn’t show. When he did, she could see he was handsome, a preppy guy in a pink polo shirt and khakis. “Paulina?” he asked eagerly. She nodded. As he smiled and pulled back the blanket draped across the stroller, he found himself surrounded, handcuffs slipped around his wrists.
“Paulina” watched his face fall, his confusion giving way to distress as FBI agents took him into custody. It was her first undercover arrest. It would be the first of many.
if one wanted to hide in plain sight, one could do no better than the tidy, suburban neighborhood on the outskirts of St. Louis, where FBI Special Agent Nikki Badolato now resides. The well-tended, two-story homes are so pleasantly indistinct that I could hardly tell you what hers looks like, even if it were safe for me to do so, which it is not. Suffice to say that Midwestern comfort and conformity unspool around every gently winding curve. Here Badolato has raised her two children, a daughter who is now in college and a son who is a junior at a local high school. When planning a neighborhood scavenger hunt or tending the community garden, Badolato does not often mention her many years as head of the Child Exploitation Task Force, a joint effort between the feds and local law enforcement that targets some of the country’s most heinous crimes. Open a cabinet in her kitchen, however, and a government-issued Glock 42 can be found stowed away between the vitamins and mixing bowls.
On a sunny morning this past October, Badolato sat at her dining room table, scrapbooks and albums spread out before her on the dark wood. There was the acceptance letter she’d received from the bureau the spring of her senior year of high school, after a representative had shown up to administer a test in the typewriting room. “I chose to wear a red dress and red heels,” she says of her first day as an FBI mail clerk, two weeks after her 18th birthday. “I don’t know what the hell I was thinking. I guess maybe I was trying to go in bold?” She pauses at a picture of herself on the gun range at Quantico almost 10 years later, her shoulders squared and her caramel hair pulled back into a ponytail as she fires off rounds. By then, she’d married a man she met just after high school, had a little girl, completed college at night, and been accepted into agent training in the heady days after 9/11. She’d seen her first dead body only a few weeks into the job, after the pursuit of a bank robber ended with a shootout in a Walmart. When Badolato got to the scene, the body was still warm, and the perp’s head was resting on a bag of cookies. “It was surreal,” she says. “How many times have you been in a Walmart and walked down Aisle 4, not really expecting there to be a dead person with his head lying on a bag of Chips Ahoy?”
Badolato wasn’t deterred. She felt like the bureau saved her, plucked her out of a shitty home life, and gave her prospects and purpose. As a new agent, she was intent on proving herself worthy. “My training agent told me, ‘You know, Nikki, it’s a marathon, not a sprint,’ ” she says. “I was like, ‘That’s ridiculous. I don’t even know what that’s supposed to mean.’ ” She turned a few pages to show a picture of the 391 kilos of cocaine and 140 pounds of meth she’d recovered on a single raid during a stint with a cartel squad, then pointed out another in which she poses with a five-year-old child she’d rescued, the little girl’s hair cut short because the kidnapper had wanted her to look like a boy. But the keepsake she really wants to find is the card that Bolen’s wife had pressed into her hand at his sentencing, the one with the picture of their children — a blond girl of about three years and a tiny baby — and the words “These are the faces of the children you protect each day.” Bolen’s wife had been the only one she’d ever encountered who had lobbied for her husband to receive the maximum sentence. Some wives accused the FBI of planting evidence inside computers. Most seemed intent on clinging to their delusions. (Attempts to reach Bolen for comment were unsuccessful.)
Which, Badolato has come to understand, is the way it goes with child trafficking and sexual abuse. She had invited me into her home — had agreed to speak on the record about her decades-long career working undercover — because when it comes to the crimes she’s spent her career fighting, she has had enough of the delusions people are under. She’s had enough of the way movies like Sound of Freedom both glamorize and trivialize the work she and her colleagues do, enough of the idea that swashbuckling white men burst through doors and rescue trafficked children with a Bible in one hand and a firearm in the other, enough of conspiracy theories about Hollywood and Washington that detract from the real root causes of why children are trafficked and abused. “Human trafficking is not the movie Pretty Woman — the girl doesn’t get the guy — and it’s not the movie Taken, where people are kidnapped in a foreign country and sold on the black market, or shipped in a container across the world,” one of the detectives who worked on Badolato’s task force tells me. “I’m not saying that doesn’t ever happen, but it’s not what we’re seeing.”
“Right now some little girl is being dropped off in the parking lot of a motel,” Badolato says. “There are four girls holed up in a hotel next to a McDonald’s. It is happening all the time.”
What they are seeing is a lot more insidious and a lot more homegrown. A report released in 2018 by the State Department ranked the U.S. as one of the worst countries in the world for human trafficking. While the Department of Justice has estimated that between 14,500 and 17,500 foreign nationals are trafficked into this country every year, this number pales in comparison to the number of American minors who are trafficked within it: A 2009 Department of Health and Human Services review of human trafficking into and within the United States found that roughly 199,000 American minors are sexually exploited each year, and that between 244,000 and 325,000 American youths are considered to be at risk of being trafficked specifically in the sex industry. Heartbreakingly, many of these children are victimized not by strangers who’ve abducted them from mall parking lots but rather by people they know and trust: Studies have found that as much as 44 percent of victims are trafficked by family members, most often parents (and not infrequently parents who were trafficked themselves). Between 2011 and 2020, there was an 84 percent increase in the number of people prosecuted for a federal human-trafficking offense. Of the defendants charged in 2020, 92 percent were male, 63 percent were white, 66 percent had no prior convictions, and 95 percent were U.S. citizens.
Badolato’s unit with a kidnapping victim after her recovery in 2011.
COURTESY OF NIKKI BADOLATO
Badolato started her career as an FBI agent in some of the earliest days that children could be bought, sold, and traded online. As the internet-porn industry mushroomed, its most lucrative branch turned out to be that of child sexual-abuse materials (the term “child pornography” is no longer used by those in the field, as it implies consent). And as demand for these images increased, so did the abuse that led to their creation.
In 2003, just a few months after Badolato graduated from Quantico, a Crimes Against Children squad was formed in the Atlanta office where she’d been stationed. By then, the FBI was starting to get a handle on the extent of the problem — if not exactly what to do about it. At a weeklong training in Baltimore, Badolato was given a tour of the darkest underbelly of fetish chat groups and then instructed to figure out how to infiltrate. “Everyone was a little nervous,” she explains of the directive. “It was a process, a direction that was new.” Agents were told that they would need to come up with a “persona” and a “story,” and that they would likely have to provide images of children to “prove” they had a minor on offer. They were also told that they could use images of their own children, if they were comfortable doing so (the FBI no longer endorses this policy).
Badolato developed “Paulina” based on her understanding that any persona would need to share most of her own backstory and traits. “That’s the only way you can really do undercover work,” Badolato says. “People can tell the sincerity in what you’re saying, so there has to be a level of genuineness, but then you just add this criminal element to it.” Most of the things Badolato had told Bolen were true: where she was from, her family background, the monstrousness of her mother, a woman who she says would pass out cigarettes and beers to Badolato’s 13-year-old friends in a state of manic permissiveness one minute and fly into a violent rage about a piece of lint on the floor the next. (Badolato’s mother declined to comment for this article, but a childhood friend corroborated Badolato’s account.) It was true that growing up in an unstable home with a string of stepdads, she had never really felt loved, true that she had divorced her first husband, true that she was raising their three-year-old daughter on her own. The only thing that wasn’t true was her tale of being molested, her initiation into the “lifestyle” — to use the chatroom parlance — that Paulina said she now wanted for her daughter. As Badolato had familiarized herself with the language and behaviors of the chatrooms, she’d honed that added criminal element, imagining what psychological conditions might believably lead a parent to traffic their own child and how those conditions could be grafted onto her real life story. She already had a history of abuse; it was not hard to extrapolate to a fictional stepfather who had seemed to provide a gentle counterpoint, showing her love and making her feel special when no one else had, even if others couldn’t understand. From there, it was easy to convince the chatroom participants that she shared their belief — or justification — that most people had it all wrong and that “child love” was natural, and could even be beneficial for the child.
Badolato estimates that she has arrested more than a thousand people; not one of those arrests has failed to end in a conviction. She didn’t know until she was in the thick of it that most agents refuse this sort of work, that most can’t even pretend to forge a relationship with someone looking to victimize a child. But she could. “Paulina,” she points out, is not a name she chose at random; it’s similar to her own mother’s name. Badolato says she had grown up learning to compartmentalize for the sake of her own emotional survival. She’d perfected the art of engaging with someone whose actions she couldn’t stand. Doing this work had felt like a way of taking her trauma and putting it to good use, of leveraging her past as a safeguard against her daughter’s and other children’s futures.
Of course there were moments that were hard to take — when suspects mentioned which brands of lubrication were best or whether or not a parent might hold a child down. There were times when she knew that even talking about these things was a turn-on for these men, times when the conversations made her nauseous, times when she’d lie awake all night or play back a recording and think, “Holy shit, I listened to this? I said these words?” But she kept faith in the mission. She reminded herself that the pictures she sent of her daughter — the beautiful, little girl sleeping in the next room — did not represent a real child on offer. “I was thinking, ‘If I send this obscure picture of my daughter and he acts on it, then he’s never going to harm my daughter or anybody else’s,’ ” Badolato says now. “I was presenting a fake girl to save a real one.”
Kyle Parks seemed to think he could get away with anything. He seemed to think, for instance, that he could get away with running a brothel, a 1-900 sex line, and a housecleaning company out of the same Columbus, Ohio, office park and under the same oxymoronic name, XXXREC and Hygiene Services. He seemed to think he could invite one young woman and five teenagers (four of whom he had only just met) on a road trip to Florida, but instead deposit them in two rooms of a Red Roof Inn in St. Charles, Missouri. When they piled out of the minivan — high on the drugs he’d given them — saw snow falling and asked to be taken home, he thought he could make a little money off them first. All it took was a few ads in Backpage — the Craigslist of sex advertisements — and men began showing up.
Even after things started going south for him, Parks couldn’t fathom that he wouldn’t prevail. When someone alerted law enforcement as to what was going on, Parks (who, according to legal documents, had been out getting food when the police showed up) burst into the precinct the next morning looking to bail his “friend” out. When questioned about the 88 condoms found in the back of his van, he said they had been prescribed to him by a doctor. After being taken into custody, he protested that he was being set up. Most people would have cut their losses and pleaded guilty, but not Parks. He thought he could take his case to court and win.
And it wasn’t impossible to imagine that he might. Badolato knew that even the tightest cases could go sideways when put before 12 people who would inevitably enter the courtroom with a cinematic sense of what sex trafficking was supposed to be. In fact, it wasn’t just the jury that Badolato knew she would need to convince; it was also often the victims themselves, young people who had internalized the exact same misconceptions about trafficking that the jury had — along with any number of other judgments society had thrown their way — and who were loath to submit themselves to a courtroom full of more judgment.
Of all of Parks’ underage victims, the hardest to pin down had been a 17-year-old we’ll call Sierra. Once she returned to Columbus, Sierra seemed to basically disappear. Calls to her mother’s number went unanswered. When one of the other victims managed to track her down in December 2016, a month before the case was to go to trial, Sierra agreed to meet Badolato on a blighted Columbus block with a string of dilapidated homes, climbing into the bureau’s Chevy Malibu with matted hair, dirty clothes, and a wary expression.
By this time, Badolato had remarried, had a second child, relocated to St. Louis, and taken over as head of the Child Exploitation Joint Task Force, which had become one of the most productive FBI teams in the country in terms of arrests and convictions. Meanwhile, as the internet streamlined the process of buying or selling any good or service, trafficking had become one of the fastest-growing criminal enterprises, estimated by the Department of Homeland Security to bring in $150 billion globally and considered by many criminals to be a superior business model: If caught, the sentences were often lighter than those for peddling drugs; and unlike crack or heroin, the same product could be “used” again and again and again.
Badolato taught her team of 20 how to do the online undercover work she’d trailblazed in Atlanta, tracking the movements of child-abuse material through the online underworld and then prosecuting those who distributed and produced it. Her new squad also initiated her in the type of undercover work it had been doing before her arrival: covert sting operations in which a detective would pose as a john, set up a “date,” and then meet said date in a hotel room fitted out with hidden recording devices while, in the next room over, a task-force team listened in, waiting for the code word that would let them know that enough evidence had been gathered for them to swoop in and shut the op down. This had proved a very effective technique for getting convictions, but Badolato’s arrival coincided with both a growing sentiment that consensual sex work had been over-criminalized and an increasing awareness that what looked like consensual sex work might actually be trafficking, no matter what the “date” professed in that hotel room.
Badolato has a tendency to say aloud the things she notices — about you, about others, about situations — observations that are not at all unkind but are perceptive enough that most people would keep them to themselves. She points out when someone deflects, and she has a sharp eye for defense mechanisms. She once casually mentions my tendency to mirror other people’s vocal and speech patterns. She is not shy about bringing up the emotional and physical abuse she says she experienced as a child, and she is quick to comment when someone is making excuses for someone else’s behavior. It was soon clear to her colleagues that Badolato brought a trauma-informed mentality to the work, a tendency to look beyond what someone was doing and instead try to parse why they were doing it. And she was relentless: While some squads did one or two trafficking sting ops a year, her team was doing four or five a month. In addition to the hotel rooms reserved for the john and the team, they would have a social worker set up in a third room, ready to offer services to the victims. They would have lookouts stationed to see who might be dropping the date off. If that date was found to be underage, the case was automatically classified as trafficking. But even if they weren’t, Badolato’s team was primed to get to the bottom of what was going on, to figure out whether they were being manipulated or coerced, and by whom.
“If I could put my hands on a pimp, that’s what I wanted,” says Jeff Roediger, a St. Louis county detective who was the “john” for many of Badolato’s sting ops and who makes clear that the team was not interested in policing voluntary sex work. “When I had those types of cases, and I knew they were being sincere with me, I wouldn’t book them,” he says. “It was all about talking to the girls. It’s not like in the movies where they come running to you. You know, ‘Thanks, you rescued me!’ It’s not like that. A lot of them try to bullshit you at first — ‘That’s my boyfriend, blah blah blah’— but once I talked to them for a while, they would become more forthcoming.”
Badolato’s unit was one of the first in the country to take on this “progressive and proactive” approach, as she puts it. Soon, St. Louis looked like a sex-trafficking capital — not because it was actually trafficking more victims than other cities but because the task force was so aggressively pursuing those cases, and classifying them as what they were. “I mean, I was working in vice for years,” says Roediger. “Back in the day, it was always ‘prostitution,’ ‘prostitution,’ ‘prostitution’ — until we started to figure it out a little bit, until we started digging a little deeper.”
Once they did, the task force found that roughly a third of the sex-trafficking victims they recovered were under the age of 17 — and they began to see the reach of the problem. Kids were being trafficked out of every hotel in the area, from the seediest roach motel to the fanciest Ritz-Carlton. They were being trafficked every time of day and by every socioeconomic group (“Before you go do brain surgery, you got to bust a nut real quick,” one underage victim told Badolato of her high-end clientele). Some of the victims were girls. Some were boys. Some were LGBTQ kids who’d been kicked out of their homes. Some were straight cis kids from the suburbs. “I tell people that I could probably name two or three [kids] in the school district they live in that have been trafficked,” Roediger says. “And they just can’t comprehend it.”
There were kids who were about to age out of foster care (a particularly at-risk group, according to those who work in the field), kids who’d run away, kids who were being sold to pay their family’s rent, or to buy their family member’s drugs. There were kids who’d sit in the hotel room, backpack at their feet, dutifully working on their math homework while agents and social workers tried to figure out what to do with them. Was their home life safe enough that they could be returned to it? Would a residential program take them? Of all the imperfect options, which would make them least likely to be trafficked again?
The one common denominator was this: They all had a vulnerability that could be preyed upon. They all lacked a safety net — societal, familial, emotional, or some combination thereof — that might have broken their fall. Mostly, their stories weren’t dramatic; they were typical American tales of neglect, of abuse doled out casually, of a steady stream of letdowns by people and institutions who should have propped them up. Badolato found that she had a knack for getting them to talk about this, for getting them to open up to her. She didn’t look like an FBI agent — at least not what they’d imagined. She spoke softly, but with authority and a slight vocal fry. And she thinks that, at some level, they could probably sense that she’d once been a vulnerable kid too, that with only a few slightly different twists of fate, she could have become a trafficking victim herself — and that she knew it. “My trauma looks different than theirs, but it’s trauma nonetheless,” she says. “And I think victims can feel that.”
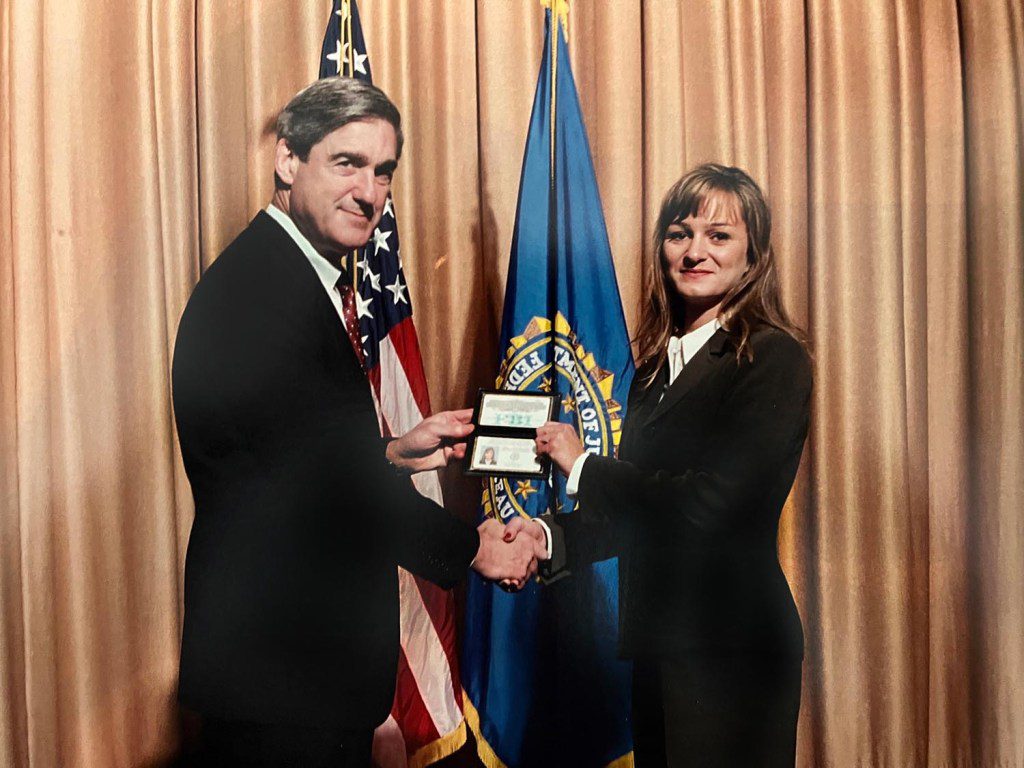

Badolato with former FBI director Robert Mueller on the day she graduated from the academy in 2002.
As the task force learned more about the psychology of victims, they also learned more about the ways in which their vulnerability was being manipulated, and how those ways were evolving. It was known in law-enforcement circles that once a skilled trafficker set his or her sights on a vulnerable young person, they could be groomed in a matter of days: one day for an introduction, a day or two to make the victim feel special and cared for, and then the day when a “friend” comes over and he needs to be “cared for” as well. Sometimes violence was involved at that point; sometimes drug use was involved throughout. But emotional manipulation was the key element, which is why it was so easy for grooming to move online, for groomers to take advantage of the false senses of connection fostered on social media.
Of the victims who are not being trafficked by family members, the majority are being groomed in this way. “I would say that probably 75 percent of the initial grooming is happening online now,” says Cindy Malott, the director of U.S. Safe Programs at Crisis Aid International. “Recruiters used to have to work really, really hard to get access to kids, but now they’re practically sitting in a child’s bedroom. And kids put everything out there — what’s going on in their life, who they’re angry about, parents are going through a divorce, their insecurities about their body, about themselves, what they do, how they spend their time — so it’s like a gift to these predators.”
The ways to manipulate are legion: Get a kid to send a compromising photo, and she’ll do almost anything to keep you from sending it out to all her Facebook friends; find out a gay kid is still closeted, and the threat of outing him gives you incredible power. And predators aren’t just on Instagram and Snapchat; they lurk in the chat functions of Roblox, Minecraft, Grand Theft Auto. “They’re everywhere,” says Malott. “People think, ‘Oh, I just got to keep my kids away from those porn sites, those horrible places.’ Well, no, predators are gonna go where the kids are.” And once there, they’re going to zero in on the kids who are most vulnerable.
That’s what got to Badolato. In her online undercover work, she’d plumbed the psychology of pedophiles, but now she wasn’t just dealing with suspects; she was spending time with victims and seeing the same vulnerabilities in them that the traffickers had seen: the instability or poverty, the addiction or mental health issues or abuse that had been normalized in their lives long before the traffickers entered them. Sometimes Badolato couldn’t help but feel that all the conspiracies and misconceptions weren’t just a distraction from the truth of trafficking but rather some sick attempt to let society off the hook for trying to solve the much more intractable problems at trafficking’s root. “People would rather stick their head in the sand than address the real problem, because then you have to face and talk about the societal issues,” she says. “With a movie like Sound of Freedom, it’s like, ‘Oh, this is in a jungle in South America. This isn’t actually in [my neighborhood].’ You know? It’s easier for people to ignore the problem than deal with the issues on a societal level.”
By the time Badolato was sitting in that Chevy with Sierra, on that blighted Ohio block, she knew that the rate of re-victimization for children who are trafficked was as high as 95 percent, according to FBI reports. She knew that 90 percent of sex-trafficking victims have a history of child sexual abuse, that more than 75 percent had lived in foster or adoptive care. She knew that she could arrest one perpetrator, and another would pop up in his place, that she could send one pimp to prison and the same victims would show up to stings some short time later, run by a different crew. She knew that testifying was a way for Sierra to psychologically push back against what had happened to her, and she was right: After the young woman took the stand on Jan. 10, 2017, Parks was found guilty and sentenced to 25 years; while testifying, Sierra had seemed to transform, to channel and embody a sort of empowerment. But Badolato also knew that once her testimony was over, Sierra would go back to that blighted block. She wondered how long that empowerment would last.
She also wondered about her own trajectory, her own ability to continue doing this work. The youngest trafficking victim she’d ever recovered from a sting op — an 11-year-old who’d been recruited through Facebook — had been returned to her family in a house that had no heat (Badolato had used an FBI slush fund to get it turned back on). One did not become immune to the human misery of such things. They compounded, became harder and harder to compartmentalize. “It’s just a combination of all of those years — and it’s all awful,” she says. “But there are particular moments that, for one reason or another, you can’t get out of your head. I just don’t think it’s in human nature to be exposed to that for so long and it not start changing who you are.”
One night, at a restaurant near where Badolato lives, I ask her whether she thinks children are being sex-trafficked right then, in that very moment, in just the mile or two radius around us. She’s quiet for a long time, her gaze fixed downward at her glass of wine. By the time she looks up, her whole body is trembling. “It’s happening right now,” she says quietly. “Right now some little girl is being dropped off in the parking lot of a motel. There are three or four girls holed up in a hotel next to a McDonald’s. It’s not only when we think about it. It is happening all the time. And if I’m just sitting here, present, having dinner, not thinking about it, that means I’m ignoring a problem that I know is real.” Tears stream down her face.
“Many images have never left my mind,” she says. “It’s really hard to have worked your entire life in law enforcement with a lot of child crime victims and be at the end of your career looking at the situation where you realize you can only do so much to make a difference.” Badolato wipes back the tears with the palm of her hand and shudders her head, as if she can shake the thoughts away. “Damn,” she says. “Fuck. I shouldn’t be the one crying. I’m not the victim of this.” The veteran agent steels herself and repeats, “I am not the victim.”
The house where Korina Ellison says she was first sex-trafficked no longer exists. It once stood on an unassuming lot in a residential suburb of Portland, Oregon, that stumbles down to the banks of the Willamette River. Now, Ellison can’t quite bring the house’s features to mind. She was so young back then, maybe four or five. There is so much she’s repressed, or only pieced together after the fact. As a child, she wouldn’t have known what she now believes to be true: that her grandmother scored her drugs by offering up her youngest daughter, Ellison’s mom. Or that, once her mom was hooked on the meth cooked by the man who’d lived in that house, she’d known just what to do to get more. But Ellison does remember being inside the house, unclothed. She does remember how the man would touch her.
Her life unspooled from there. Her father died of a heroin overdose when she was six. Her mom lost custody for good. She bounced around foster care, then various residential institutions, then whatever shelter she could find. In the story she tells of how she was sex-trafficked again in her teenage years, there’s no moment of drama, no kidnapping, no clear coercion. There was just a random, rainy afternoon when she had no place to go and was alone in the street and a car pulled up. The man inside took her home with him, fed her, introduced her to his girlfriend. They took her shopping. They let her stay. When men showed up at the home to have sex with the woman, Ellison was invited to watch, but she wasn’t expected to participate — not at first, anyway. According to a statement Ellison later made to law enforcement, she just “realized that people aren’t going to take care of [me] for free.” Soon, the woman was posting Ellison’s services on Backpage — $150 for half an hour, $200 for a full one — and the trio were traveling the Midwest. For a long time, it didn’t even occur to Ellison, then 16, to leave. “Where would I have gone?” she asks. “I’d been missing for over a year. Nobody was looking for me.” When the man told her to call him “Daddy,” she complied.
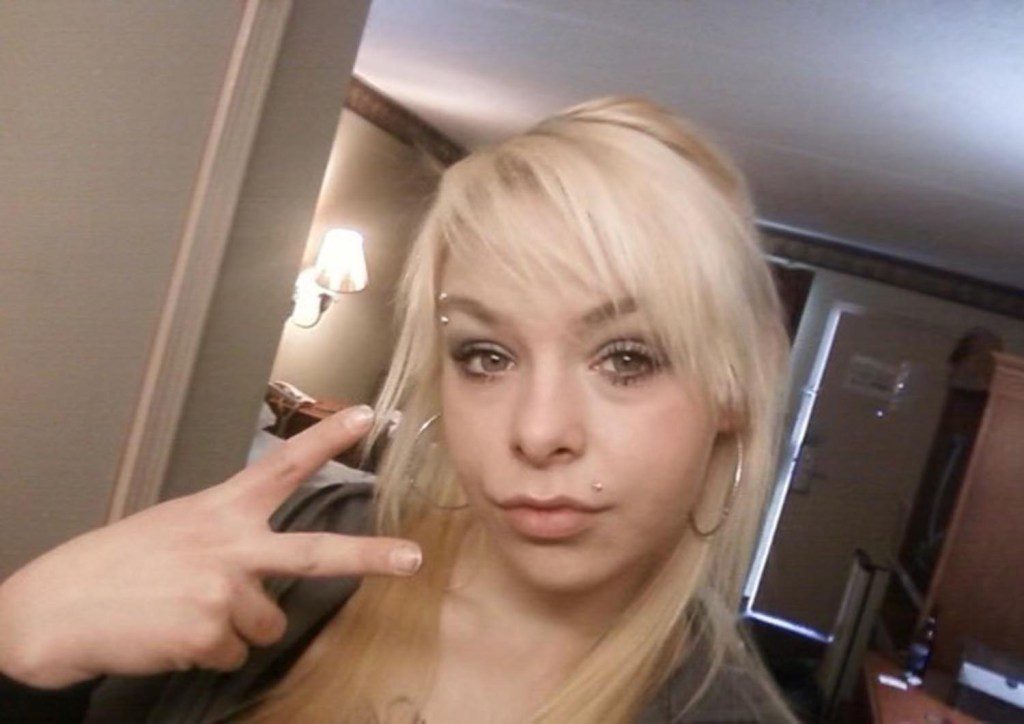
Korina Ellison, a trafficking survivor, around the time she was recovered by Badolato’s task force.
Courtesy of the subject
That was more than a decade ago, near the beginning of Badolato’s tenure as head of the Child Exploitation Task Force. But by 2021, leaving it had seemed a necessary form of self-preservation. One of her last cases had gone well legally: The perp, a retired police officer from California who had produced child sex-abuse materials of three sisters in Manila, had pleaded guilty to such charges when he learned that Badolato had brought the girls to the states to testify against him. But the experience had been emotionally devastating for Badolato, who had wanted the sisters, then 16, 13, and 11, to have memories of the U.S that consisted of more than reliving their trauma in a courtroom. She took them shopping and to the zoo, invited them to her home to have dinner with her own family, saw them slowly start to open up and laugh and behave like the children they were. Then she’d had to put them on a flight back to Manila, back to the aunt who had allowed the man to abuse them and who Badolato had been unable to extradite. Fortunately, she says, their estranged father ended up intervening and taking custody of the girls, but that feeling of futility in the fight lingered.
“If I can be perfectly honest,” Badolato says, “I truly don’t believe that the FBI realizes what they put their agents through doing that kind of work.”
“I stayed for a little bit longer after that trial, but it really was when I should have been able to look myself in the mirror and say, ‘Nikki, you’re done,’ ” Badolato had told me in St. Louis. “It became clear that I had been doing it too long.” She’d spend the last couple of years working national security, a position without the immediacy of child-exploitation work, but also without the heartache. “If I can be perfectly honest, I truly don’t believe that the FBI realizes what they put their agents through doing that kind of work. I just don’t,” she says.
And yet, here Badolato was in Portland, leading Ellison, now 30, up to her hotel room, telling her about all the announcements she’d heard in the Atlanta airport instructing travelers to be on the lookout for sex trafficking. “It’s like white noise in the background,” she says as Ellison settles into the sofa. “It’s a false sense of doing something to help.”
“Here’s the thing: Nobody knows what to look for,” Ellison agrees.
“And what about the victims who are in that airport, who are walking around and listening?” Badolato asks.
“I wouldn’t have even heard that announcement,” Ellison replies. “Because I didn’t feel like a victim. It goes a lot, lot, lot deeper than anybody realizes.”
That’s what she and Badolato both understand. That’s why they started talking eight months ago. Of all the teenage victims Badolato’s task force recovered, Ellison is one of the few who she knows has permanently extricated herself from being prostituted, though it took years for her to get to that point, years for her to see that what happened to her was not her fault but rather a fault in the system, a fault in many systems over the course of generations. Neither she nor Badolato can fix that.
Yet they can’t help feeling like there’s something they can fix — or at least try to. Under the umbrella of an organization she’s founded called Innocent Warriors, Badolato created a program for schools, instructing educators on the signs that might indicate a student is being trafficked and teaching kids how to avoid getting groomed online, which, she believes, is not about stranger danger but rather an awareness of subtle manipulation. Ellison has been working with trafficked youth through nonprofits like Children of the Night, the residential program where Badolato’s team sent her when she was 17. Together, they’ve been talking about having Ellison help train undercovers who are learning to do trafficking sting ops. They’ve also discussed starting a mentorship program in which children who are still being sex-trafficked are paired with young adults like Ellison who once were, providing a way for victims to begin to envision a different future for themselves and a path toward it even while being prostituted. Such a program may be retroactive rather than proactive, but it would capitalize on Badolato’s and Ellison’s experience and expertise — and it could help in the healing of mentors and mentees alike.
Badolato had traveled to Portland for the two to talk face-to-face about how the program might work. “You have to understand how they’ve been traumatized because sometimes, to a child, relating doesn’t sound like you’re relating. It sounds like you’re pointing out all the bad things in them,” says Ellison from the driver’s seat of her Nissan Pathfinder as she drives Badolato around to show her certain landmarks of her past after she’d left Children of the Night: the bridge she’d slept under for over a year after a boyfriend had gotten her hooked on heroin, the blocks downtown where she’d bounced between a children’s shelter and the needle exchange. It had taken a prison sentence for her to finally break her addiction and commit to a different kind of life, though that evolution had had less to do with not having access to drugs than with seeing her own mother cycle in and out of the same facility — like looking into her own future and witnessing how bleak it would be. Maybe, she thought, she could provide the inverse of that for kids in Innocent Warriors. Maybe she could reverse engineer her own escape.
“I just want to make it very clear that if you were a victim, you are a victim, and just to not have any shame in that,” she tells Badolato as they drive through Portland’s misty streets.
“What I anticipate and hope is that then we get survivors that are like, ‘They get it,’ ” Badolato replies. “And that it opens up doors to help, for people to recognize that there are people who get what’s really going on.”
“It took a really long time for me,” Ellison says of coming to terms with her own victimhood.
“It’s like reworking your thought process about some of those things,” Badolato agrees. “And that’s hard, and it happens slowly over time, and it looks different for everybody.”
Ellison grips the wheel tightly. “The truth does matter. It does. The truth is the fucking truth. And it’s been empowering to be able to talk about it because that’s another way that I’ve realized, like, ‘Man, I was a victim,’ is re-going over all of this. Because when it happens so many times, you do blame yourself. It’s a lot easier to just continue to live in a lie than believe that you were lied to.”
Still, Ellison and Badolato agree that the impressionability that makes children vulnerable is also what makes them open to guidance and mentorship if a relationship of trust can be established. “What do you think a parent does? They groom you. I’d been waiting to be guided and groomed,” Ellison says.
It’s been instructive to see that potential from another perspective, as a mother doing the guiding. As the afternoon wears on, Ellison stops to pick up her then-15-month-old son, who was being watched by a social-worker friend. She buckles the little boy into his car seat, ruffles his hair, and passes him a bottle. He grins widely and begins removing his shoes and socks, throwing them gleefully onto the floor of the car and then kicking his tiny feet in time with the music as Ellison glances back at him and smiles. “Kids are so perfect,” she says.
The last stop of the day is the large plot of land where the drug dealer’s house once stood. Now, it’s been turned into a playground, with brightly-colored jungle gyms, a covered picnic area, and a large lawn, where a couple leisurely walks their dog. Ellison and Badolato climb down from the car and stand at the park’s edge, as Ellison’s son toddles around the grass, oblivious to what had transpired in that very spot. There is some form of poetic justice in the land being earmarked for children’s enjoyment, but neither woman voices it. Mostly, they’re quiet. Night is falling, the air growing cooler, and the gray sky fading into dusk.
“You would never think a park could hide what it used to be,” Ellison says at last. And yet it did. Driving off with Badolato at her side and her son babbling happily in the back seat, Ellison glances in the rearview mirror, but only for a moment. Badolato keeps her eyes fixed only on the road ahead.
If you or someone you know may be involved in trafficking, call the toll-free National Human Trafficking Hotline at 888-373-7888, text the hotline at 233733, or talk online at humantraffickinghotline.org/chat.





